The manufacturing industry is undergoing a transformative phase with the adoption of automation. From robotics to artificial intelligence, automation is not just a trend but a necessity for businesses to stay competitive in a rapidly changing global market.
This article explores the role of automation, its benefits, challenges, and actionable strategies for small manufacturers, supported by data and real-world examples.
Why Automation Matters in Manufacturing
Automation improves productivity, reduces errors, and enhances safety in manufacturing processes. A McKinsey report estimates that automation could boost global productivity by 0.8% to 1.4% annually. Additionally, the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) highlights that industrial robots alone can reduce labor costs by 16% in highly automated sectors.
For small manufacturers, automation offers an opportunity to level the playing field, enabling them to compete with larger players by increasing efficiency and agility.
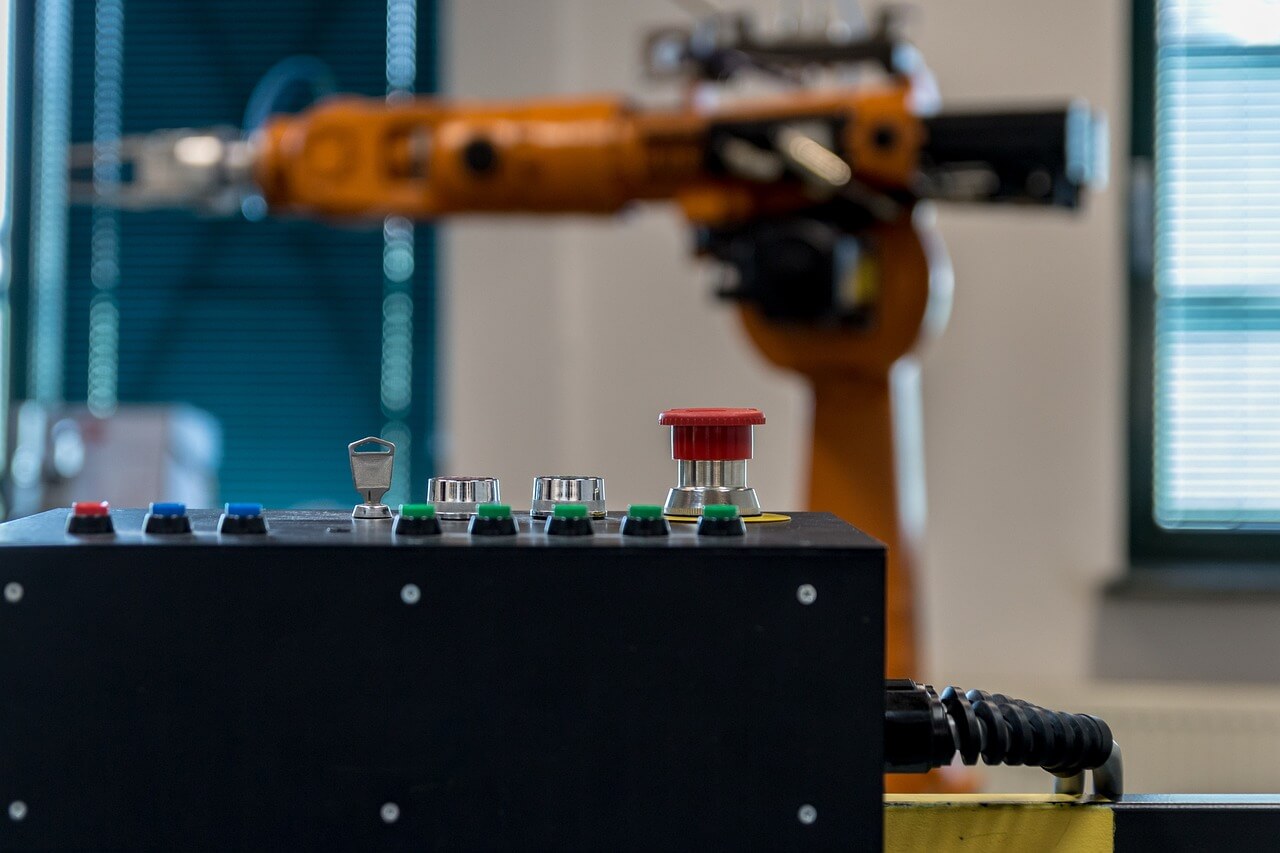
Key Technologies Transforming Manufacturing Automation
- Robotics and Cobots
Industrial robots have revolutionized manufacturing, performing repetitive tasks with precision. Collaborative robots (cobots), designed to work alongside humans, are becoming increasingly popular for their affordability and ease of integration. For instance, Universal Robots’ cobots have helped businesses automate tasks with minimal disruption. - Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI-driven solutions like predictive maintenance reduce downtime by analyzing machine data to anticipate failures. According to a PwC study, predictive maintenance can lower maintenance costs by 20% and downtime by 50%. - Internet of Things (IoT)
Smart factories leverage IoT to connect machines, sensors, and systems, allowing real-time monitoring and optimization. Siemens’ MindSphere is an example of how IoT platforms improve operational efficiency. - Emerging Trends:
- Affordable Automation Tools: Companies like Fictiv offer cloud-based manufacturing platforms, making advanced automation accessible to smaller manufacturers.
- Energy-Efficient Automation: Innovations like energy-saving robotic arms align with sustainability goals.
Benefits of Automation for Small Manufacturers
- Increased Productivity: Automating repetitive tasks allows human workers to focus on more complex roles, boosting overall output.
- Cost Savings: Automation reduces labor costs, minimizes waste, and enhances resource utilization.
- Improved Quality: Automated systems ensure consistency, reducing defects and improving customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced Safety: Robotics handle hazardous tasks, minimizing workplace injuries.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Financial Constraints
Many small manufacturers struggle to afford automation. Solutions include exploring leasing options, grants, and government incentives. For example, the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) offers loans for technological upgrades. - Bridging the Skills Gap
Automation requires a skilled workforce. Investing in training programs, like those offered by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), can help upskill employees. - Change Management
Resistance to change is common. Engage employees early, highlight the benefits, and provide hands-on training to foster acceptance.
Actionable Steps for Small Manufacturers
- Start Small: Automate one process at a time to test feasibility and measure ROI.
- Invest in Training: Equip your workforce with the skills needed to operate and maintain automated systems.
- Leverage Subscription-Based Tools: SaaS solutions lower upfront costs and provide flexibility.
- Collaborate with Partners: Work with technology providers to customize solutions for your business.

Future Trends in Automation
- Subscription-Based Robotics: Companies like Formic Technologies offer robots-as-a-service, eliminating the need for capital investment.
- AI-Driven Supply Chains: Predictive analytics will optimize inventory management and reduce lead times.
- Sustainable Automation: The focus on green manufacturing will drive innovations in energy-efficient and recyclable automation tools.
Real-World Case Studies
- Foxconn: The electronics manufacturer deployed 10,000 robots in its assembly lines, significantly reducing production time.
- SME Success Story: A small furniture manufacturer integrated cobots into its production process, doubling output within a year without increasing its workforce.
Balancing Automation and Human Workforce
Automation does not replace humans but complements them. By reskilling workers and focusing on collaborative roles, manufacturers can create a harmonious balance between technology and the workforce.
Conclusion
Automation is reshaping the manufacturing landscape, offering immense benefits for businesses of all sizes. By embracing emerging technologies, addressing challenges proactively, and leveraging actionable strategies, small manufacturers can harness automation to achieve sustainable growth and remain competitive in an evolving market.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is automation in manufacturing?
Automation in manufacturing refers to the use of advanced technology, such as robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), to streamline production processes. These technologies enable tasks to be performed with minimal human intervention, improving efficiency, precision, and productivity.
2. What are the primary benefits of automation in manufacturing?
Key benefits include:
- Increased Productivity: Automated systems operate continuously without breaks, boosting output.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Machines reduce human error, ensuring consistent quality.
- Cost Savings: Reduced labor and energy costs contribute to long-term savings.
- Improved Workplace Safety: Automation handles dangerous tasks, reducing the risk of injury.
- Scalability: Flexible systems can adapt to changing production needs quickly.
3. What technologies are driving automation in the manufacturing sector?
Some key technologies include:
- Industrial Robots: Robots perform repetitive or precision-based tasks with high efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI analyzes data to optimize processes and predict maintenance needs.
- IoT Devices: IoT sensors provide real-time monitoring and data exchange for smarter systems.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Customizable, efficient production methods.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Transport materials autonomously within facilities.
4. How does automation impact employment in manufacturing?
Automation often replaces repetitive and manual jobs but also creates new roles requiring technical expertise, such as programming, maintenance, and oversight of automated systems. Upskilling employees is essential to bridge this transition and ensure they remain integral to the industry.
5. What challenges do manufacturers face when adopting automation?
Some common challenges include:
- High Initial Investment: The cost of purchasing and implementing automation systems can be significant.
- Integration Complexity: Combining new technologies with legacy systems can be difficult.
- Skill Gaps: Employees need training to handle advanced technology.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Automated systems connected to the internet are vulnerable to cyberattacks.
- Maintenance Costs: Keeping systems operational requires ongoing technical support.
6. Can small businesses benefit from automation?
Yes, small businesses can benefit by starting with cost-effective, scalable solutions such as collaborative robots (cobots) or software-based automation tools. Gradually adopting automation can enhance productivity, improve quality, and reduce waste, providing a competitive edge.
7. What role does sustainability play in manufacturing automation?
Automation promotes sustainability by:
- Reducing Waste: Precise processes minimize material wastage.
- Energy Efficiency: Smart systems optimize energy usage.
- Recycling Capabilities: Automated systems can enhance recycling and repurposing of materials.
8. How is artificial intelligence transforming manufacturing automation?
AI empowers automation by:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI detects potential equipment failures before they occur.
- Process Optimization: AI analyzes production data to improve efficiency.
- Quality Control: Machine learning identifies defects in real time during manufacturing.
9. Are there industry-specific applications of automation in manufacturing?
Yes, automation is tailored for various industries:
- Automotive: Automated assembly lines and welding robots.
- Food & Beverage: Automated packaging and quality control systems.
- Pharmaceuticals: Precision drug manufacturing and packaging.
- Electronics: Circuit board assembly and testing.
10. What is the future of automation in manufacturing?
The future includes:
- Hyper-Automation: Integration of AI, robotics, and IoT for fully automated systems.
- Human-Machine Collaboration: Cobots working alongside human workers.
- Advanced Analytics: Data-driven decision-making to improve processes.
- Green Manufacturing: Automation supporting eco-friendly production methods.
By leveraging automation, manufacturers can not only achieve operational efficiency but also position themselves to thrive in an increasingly competitive market. Transitioning to automation requires a strategic approach, but the long-term benefits are immense for businesses of all sizes.
Discover more from Grow and Succeed Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.







Dear Daisy,
Very well said !
Thanks for liking my post on Children ! ♥️
Dear Ma’am, please neglect earlier comment,
Very well said !
Thanks for liking my post on Children ! ♥️
Dear Esther Ma’am,
You are a great writer. It’s my great pleasure to read your posts.
Thanks for liking my post on Diary ♥️
Thank you so much. I appreciate your sweet words. ❤